Computing leaky waves in semi-analytical waveguide models by exponential residual relaxation
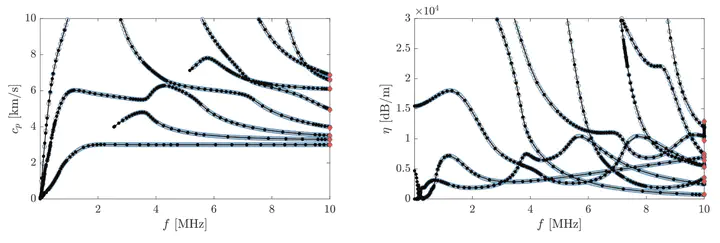 Dispersion of a titanium plate radiating into teflon and brass.
Dispersion of a titanium plate radiating into teflon and brass.Abstract
Semi-analytical methods for modeling guided waves in structures of constant cross-section yield frequency-dependent polynomial eigenvalue problems for the wavenumbers and mode shapes. Solving these eigenvalue problems over a range of frequencies results in continuous eigencurves. Recent research has shown that eigencurves of differentiable parameter-dependent eigenvalue problems can alternatively be computed as solutions to a system of ordinary differential equations (ODEs) obtained by postulating an exponentially decaying residual of a modal solution. Starting from an approximate initial guess of the eigenvalue and eigenvector at a given frequency, the complete eigencurve is obtained using standard numerical ODE solvers. We exploit this idea to develop an efficient method for computing the dispersion curves of plate structures coupled to unbounded solid or fluid media. In these scenarios, the approach is particularly useful because the boundary conditions give rise to nonlinear terms that severely hinder the application of traditional solvers. We discuss suitable approximations of the nonlinearity for obtaining initial values, analyze computational costs and robustness of the proposed algorithm, and verify results by comparison against existing methods.